Purchase Orlistat OTC.
Orlistat is primarily used in the management of obesity, including weight loss and weight maintenance when combined with a reduced-calorie diet. It also contributes to the reduction of the risk of weight regain after prior weight loss. Here, we delve into the conditions treated with Orlistat, analyze its effectiveness, and compare it with other weight-loss medications.
Diseases Treated with Orlistat
Orlistat is specifically indicated for:
Obesity Management: It aids in weight loss and helps maintain this loss. It’s particularly effective when integrated into a comprehensive weight management program that includes diet, exercise, and behavioral changes.
Risk Reduction: It’s known to reduce the chance of weight regain and positively affects various obesity-related risk factors and diseases, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and heart disease.
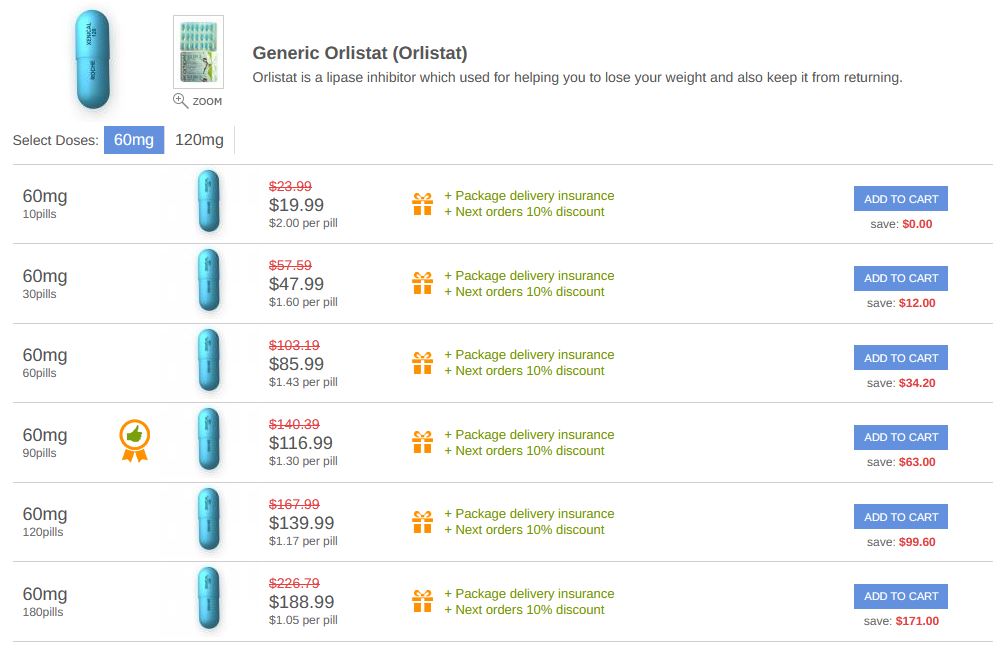
Buy Orlistat over the counter.
Online purchase of Orlistat. Favorable offer for buying over the counter. To order Orlistat, follow the advertising link and order at a favorable price. Buy Orlistat over the counter, this is the most economical and safe solution.
Treatment Outcomes with Orlistat
Weight Loss Efficacy: Studies have consistently shown that Orlistat, when used along with lifestyle changes, can lead to significant weight loss. The amount of weight loss achieved with Orlistat is usually modest but can be significant enough to lower the risks of developing obesity-related diseases.
Long-Term Weight Management: Patients taking Orlistat have demonstrated better weight maintenance and less weight regain compared to those who rely on lifestyle changes alone.
Impact on Obesity-Related Conditions: Orlistat has been linked to improvements in obesity-related conditions, such as lower total cholesterol levels, improved glycemic control in diabetes, and reduced blood pressure.
Comparison with Alternatives
When compared to alternative weight-loss medications or supplements, Orlistat has unique characteristics:
Mechanism of Action: Unlike systemic appetite suppressants, Orlistat works locally in the gastrointestinal tract to inhibit fat absorption. This targeted mechanism minimizes systemic side effects and focuses on the dietary fat as the primary source of calorie reduction.
Clinical Efficacy: While alternatives like Phentermine-Topiramate, Liraglutide, or natural supplements are available, Orlistat remains a favored option due to its proven efficacy, especially in individuals who respond well to fat-reduction strategies in their diet.
Side Effects Profile: Orlistat’s side effects are mostly gastrointestinal and related to its fat-blocking mechanism, which are generally considered manageable. In contrast, systemic medications may have broader side effect profiles, affecting a wider range of body systems.
Making the Right Choice
Selecting the appropriate weight loss treatment, including Orlistat or its alternatives, depends on individual health profiles, the presence of comorbidities, and personal preferences. Consulting with healthcare professionals is crucial to decide on the most suitable and safe weight management strategy.
Conclusion
Orlistat offers a viable and effective option for obesity management, particularly for individuals committed to a lifestyle of reduced calorie intake and regular physical activity. Its distinct mechanism of action and favorable safety profile make it a unique tool in the weight loss arsenal, differing from systemic alternatives in both its benefits and challenges. Patients should weigh their options carefully, considering their specific needs and medical history, to choose the best path toward achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.